Today’s supply chain networks have become extremely complex. From procurement to manufacturing and distribution, the supply chain networks involve a huge number of transactions. It’s a multi-tiered system that involves manufacturers, suppliers, logistics partners, payment partners, retailers, customers, and many more. There are complex supply chain networks that span over multiple continents, hundreds of stages, and multiple points of payments and transactions. Such complex supply chain systems lack transparency, making it difficult for the parties involved to track the transactions in real-time. The system also fails to provide the customers or end-users visibility regarding the authenticity and the appropriate value of the product they’re buying. As a quick fix to all these complexities, blockchain technology has the potential to transform modern supply chains with its intrinsic features like trust, transparency, and security.
According to its evangelists, blockchain technology is capable of transforming any business from top to bottom. But, to what extent can blockchain technology support supply chain management? Many pilot projects have already been tested, but there’s only limited evidence to prove blockchain technology’s effectiveness. Let’s discuss the role of blockchain technology in SCM and 5 successful blockchain-based supply chain projects.
How blockchain is revolutionizing supply chains
Blockchain is a distributed ledger technology that allows users to verify and validate transactions. A copy of the immutable ledger is available for all the parties in the network. Initially used for cryptocurrency transactions, blockchain is now being used for enterprise uses. Some of its use cases include, digital transactions, automation of contracts and agreements, track and trace, and payments, etc. Moreover, the technology offers the highest level of security with its consensus mechanism and encrypted ledger of transactions.
Blockchain technology can be a solution for most of the challenges the modern supply chain networks are facing. It makes the network transparent and helps to build more trust among the parties involved. The consensus mechanism ensures that all the stakeholders are on board while making a transaction. Validation is required from all the concerned parties for payments, deliveries, transportation of goods, etc. The ledger is immutable making it difficult for anyone to conduct fraudulent activities like false transactions, changing inventory records, etc. Blockchain technology also helps to track and trace materials in near real-time. Every party with permission will have a copy of the ledger, ensuring transparency and accountability. This helps to build trust and reduce disputes during transactions.
Top supply chains powered by Blockchain technology
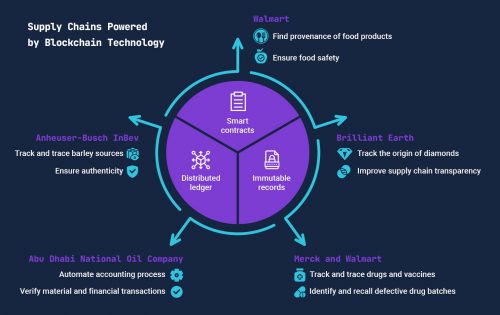
1. Walmart: Enhancing the food supply chain
As food security and food-borne diseases became increasingly important concerns for consumers, Walmart decided to address this issue by transforming their food supply chain into one that is more transparent. Realizing the power of blockchain technology, Walmart partnered with IBM to build a Hyperledger Fabric-based blockchain application that will track food back to where it was originally manufactured. Each node on the blockchain network represents an entity that handled the food on its way to the store. This makes the whole network visible and ensures that a defective batch of products is not sold. Initially, two proof of concept projects were run to track the provenance of mangoes sold in the US and the pork supplies in China. The blockchain system helped to bring down the time to track down the origin of mangoes from 7 days to an impressive 2.2 seconds. The POC project for tracking pork in China enabled suppliers to upload the certificates of authenticity to the network, thereby ensuring food safety.
2. Brilliant Earth: Ensure ethical diamond sourcing
Brilliant Earth, one of the top diamond jewelry brands, has partnered with Everledger to help improve visibility in the diamond supply chain. The partnership aims to track the lifecycle of diamonds sold online. A blockchain-enabled badge is added to diamonds, and customers can view details like provenance, carat weight, cut process plans, and more. As soon as a sale is complete, the ownership transfer of the diamond is recorded in the immutable blockchain network. Integrating blockchain technology into the diamond supply chain has enabled transparency in the network. Customers can now see where and how their diamond was sourced, ensuring authenticity and trust.
3. Anheuser-Busch InBev: Track and trace barley in used in beer
AB InBev, the biggest name in the brewing industry, has partnered with SettleMint, a blockchain as a service company to pilot blockchain technology for tracking its barley supply chain. The Belgian beer maker is one of the world’s top users of barley. Its supply chain is extremely complex and spans 13 countries across all 5 continents. AB InBev manages 60% of its barley supply directly, while the blockchain pilot project is designed to trace the remaining 40% of barley coming from different European countries. The blockchain-powered system will allow beer drinkers to trace the authenticity and origin of the barley used in their beer by scanning a QR code on the package. The system will help AB InBev increase customer trust in its brand.
4. Abu Dhabi National Oil Company (ADNOC): Automate accounting and track oil supplies
ADNOC joined hands with IBM to develop a blockchain application that could increase transparency among their 14 group companies operating independently. The system is designed to track the finances involved and quantities of oil, natural gas, and other petroleum products in each transaction from its origin to the customers. The blockchain networks also helped ADNOC to automate their accounting process, enabling every group company to view their accounts in real-time. The blockchain implementation allowed ADNOC to improve their transparency. Abdul Nasser Al Mughairbi, ADNOC Digital Unit Manager said, “Blockchain is a game-changer. It will substantially reduce our operating costs by eliminating time-consuming and labor-intensive processes, strengthen the marketing and trading of our products, and create long-term sustainable value that will ensure that ADNOC delivers on its 2030 smart growth strategy.”
5. Merck and Walmart: Track and trace drugs in the supply chain
To protect consumer health, US Congress passed the Drug Supply Chain Security Act (DSCSA) in 2013. The act requires all pharmaceutical companies to serialize their drugs and make them traceable for security. Merck, Walmart, IBM, and KPMG formed an alliance to develop a blockchain solution to track and trace prescription drugs and vaccines sold in the USA while complying with the DSCSA. A successful pilot project was run on IBM’s blockchain and Merck’s serialization system. The project work flow and UI design were managed by KPMG. The pilot project proved to be successful in tracking drugs’ origins. The process of tracking and notifying pharmaceutical companies about defective batches, which typically took around 3 days, was brought down to a few seconds. The project demonstrated that blockchain technology can transform the pharmaceutical supply chain and ensure patient safety.
Wrapping up
Blockchain technology is changing the supply chain as we know it. While it may not be the solution to every supply chain problem, it’s certainly helpful in solving ones that deal with tracking, information flow, and payments. The cases discussed above show that blockchain can help virtually any industry, from precious commodities like diamonds to everyday items like food. Blockchain technology will certainly evolve over the coming years, and early adopters are going to reap huge rewards. There are companies offering blockchain as a service, which help businesses adopt blockchains. Yes, there are hurdles to the widespread adoption of this technology, but the examples mentioned above show a positive sign that blockchain technology is set to remove those barriers in the future.
 Anantha Krishnan Aspiring author, creative marketer, and product marketer by trade, plans, creates and promotes strategic content to reach the target audience |
